Our Approach
What is Life Cycle Assessment?
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a powerful tool for modeling the sustainability of your product or package. From extraction of materials to disposal at end-of-life, LCA helps to identify your environmental impact at every stage of the product and package life cycle.
Why is LCA Useful?
Hotspot Analysis
LCA highlights areas that will improve your impact the most
External Communications
Marketing Claims
Third party reviewed LCAs can be used to communicate the sustainability of your product or package
Certifications
LCAs can also be used to verify information for certifications such as EPDs (Environmental Product Declarations)
Eco-Modulations
Certain EPR eco-modulation programs, like Oregon’s bonus scheme, may require a 3rd party reviewed LCA to verify the impact of your product or packaging
Life Cycle Phases
*Hover over each phase for more information

MATERIAL
The materials used in the creation of a product or package. Includes transportation associated with extraction of raw materials.
MANUFACTURING
The manufacturing processes used in the creation of a product or package.
TRANSPORTATION
Inbound and outbound transportation of a product or package.
USE
Associated with products, rather than packaging, except for in the case of reusables. In this case the use phase considers washing cycles as well as transportation associated with reuse and refill.
END-OF-LIFE
The end-of-life impacts of a packaging solution are modeled using the cut-off method. The cut-off method only attributes the environmental impacts directly caused by the selected product or package, such as landfilling, waste to energy, or composting end-of-life dispositions. Includes transportation associated with the end of life disposition.
Methodologies Offered In COMPASS
COMPASS Standard Indicators
Fossil Fuel Use (MJ Deprived)
Considers the total quantity of fossil fuel consumed throughout the life cycle.
Global Warming Potential (kg CO₂ eq.)
The total quantity of greenhouse gasses (GHG) emitted throughout the life cycle. Considers global warming potential for a 100-year timeframe.
Global Warming Potential with CO₂ Uptake (kg CO₂ eq.)
The total quantity of greenhouse gasses (GHG) emitted throughout the life cycle. Considers global warming potential for a 100-year timeframe and includes the climate carbon feedback and accounts for carbon sequestration and biogenic carbon emissions.
Water Consumption (with Scarcity) (m³ world-eq.)
Represents the relative available water remaining per area in a watershed after the demand of humans, aquatic ecosystems, and manufacturing processes has been met, compared to the world average.
Mineral Resource Use (kg deprived)
Represents the availability of mineral resources and the impact of their depletion on future populations.
Freshwater Eutrophication (kg PO₄ eq.)
Emissions of phosphorus compounds released during the production of materials, which contribute to higher eutrophication in freshwater systems. Eutrophication is the abnormal increase in chemical nutrients that causes excessive plant/algal growth and decay resulting in an anoxic condition in freshwater systems, the major consequence being algal blooms.
Freshwater Ecotoxicity (CTUe)
The measure of the ecotoxicity impact of chemical releases to air, water, and land using aquatic toxicity factors.
Human Impact (Midpoint) (CTUh)
The quantity of short-term environmental emissions resulting in cancer and toxic non-cancer impacts to humans released throughout the life cycle.
Carbon Accounting Methods
Product Carbon Footprints (PCFs)
Scope 1, 2, and 3
Environmental Footprint (EF) Method
A globally-recognized LCA methodology that utilizes 16 indicators ranging from climate change and water use to particulate matter and acidification. It was created by the European Commission in 2013 and aligns with EU policy requirements.
For more information on the EF Method in EcoImpact-COMPASS, contact us.
Go Beyond GWP
Trayak's Trusted Sustainability Process
How can you see your initiatives through to the end? Explore Trayak’s trusted sustainability process, a field-tested method for holistic product and packaging sustainability below.
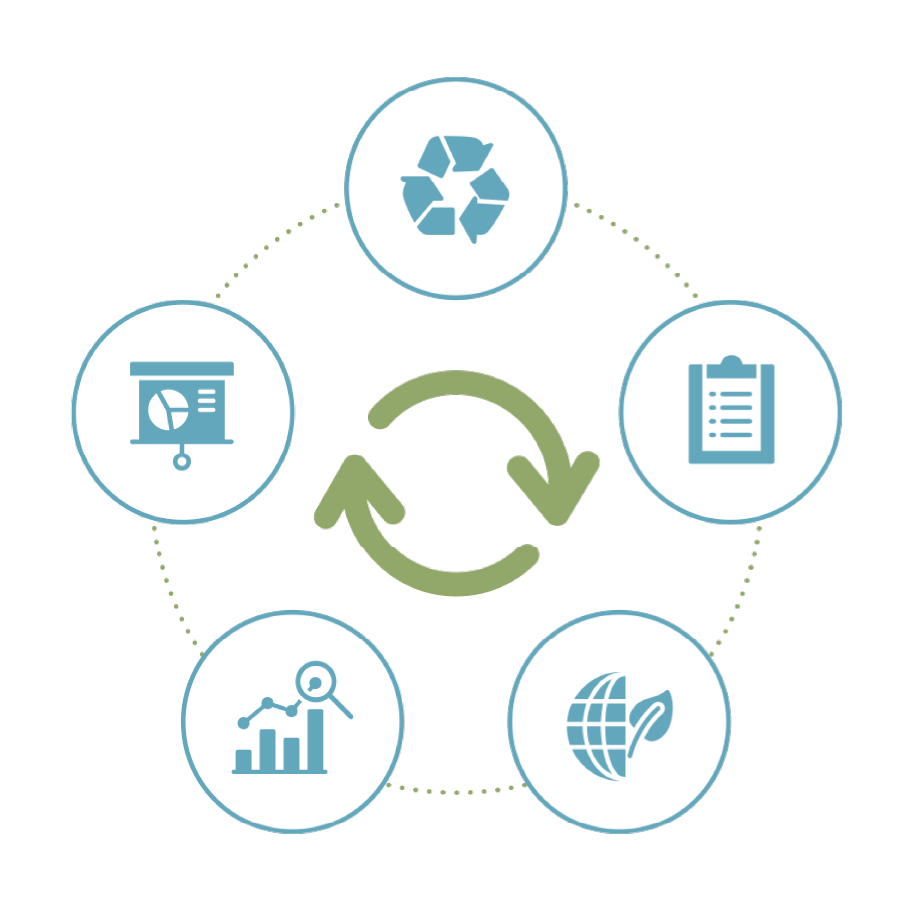
Determine Goals
Benchmark Portfolio
Improve Impact
Track Progress
Analyze and Report
Our Vision
Implementing sustainable practices into your current manufacturing and design processes is easier than it seems. Trayak’s vision is that all companies will design and manufacture their entire portfolio using sustainable strategies.
Our Mission
Trayak’s mission is to embed sustainability in your company’s mainstream product design, manufacturing, and launch processes. Partner with Trayak to harness the power of innovation and improve your impact on the environment.
Brand Story
Every brand should have a story. Here is ours.
The name Trayak is loosely defined from Sanskrit as “The Protector.” This concept has been the driving force for Trayak as a company, and it is reflected through our brand icon.
We are driven to protecting our earth by embedding sustainable practices through our customers. This is our purpose every day. When we work with customers, we offer them protection — from wasted material, inefficient manufacturing methods, and lost revenue. As our mission states, we bring real innovation to product sustainability throughout the product life cycle for our customers.
For our employees, we enable them to create and share their ideas. We encourage their passion for protecting the earth in all of their work.
We welcome you to join us on our journey to protect our environment!
